Covered Put
Direction: Bearish to Neutral
Strategy Description
Covered Put option is an option trading strategy in which you short stock and sell Out-of-The-Money put options in proportion to the shares shorted. It is also known as a Married Put option strategy.
The selling of put option is usually done on a monthly basis as a mean to collect rent while you short sell the underlying stock.
Covered Put = Short Stock + OTM Short Put
Outlook: With this stock option trading strategy, your outlook is bearish to neutral.
You are expecting a mildly drop in the underlying stock price and/or a drop in volatility.
Risk and Reward
Maximum Risk:
- Unlimited if the stock price rises.
Maximum Reward :
- Limited. Occur at expiration date when the underlying stock is at or below the strike price and the options are exercised.
= [Stock Price Shorted – Put Strike Price] + Put Premium Collected
Breakeven :
- Stock Price Shorted add Put Premium Collected.
Net Position:
- This is a net credit trade as you received a credit for shorting both the put and the underlying stock.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Can profit from three scenarios: underlying stock price drop, move sideways, or rises by a relatively small amount.
- Ability to generate monthly income.
- Earn interest on the proceed collected from shorting the underlying stock and put options
Disadvantages:
- Limited upside potential if the underlying stock drop.
- Unlimited downside risk if the underlying stock rises and the premium collected will only be a small consolation.
Exiting the Trade
Stock price drop below the strike price
- The put options sold will be exercised and you will be assigned to buy the stock. As you have already short the stock earlier, this will be similar to ”Sell High, Buy Low” and the maximum profit is realized
Stock price rise above the strike price but below the initial shorted price
- Let the options expired worthless and retain the entire option premium collected.
- Sell another put option expiring in the next month to earn additional premium. In this case, you have already earned premium from the previous put sale, and you can earn additional premium from the second put sales, and so on. This process can be repeated every month, every couple of months or every quarter. Thus further reduce the risk of the underlying short stock.
If the stock price soar above the initial shorted price
- If the stock price soar, you may cut your losses by buying back the options that you sold and stocks that you have shorted in the first place. This can be done anytime prior to expiration date. In this case, the option premium cushion the losses incurred from stock rises and you are better off then simply shorting the stock.
Covered Put Example
Assumption: XYZ is trading at $62.50 a share on Mar 20X1 and you shorted 100 share of XYZ at $62.50. You would like to earn additional income from XYZ and don’t mind buying back the stock to close off the position at a profit.
In this case, you may consider to sell one Apr 20X1 $60 strike put at $2.20 to earn an additional income. Note: commissions are NOT taken into account in the calculation.
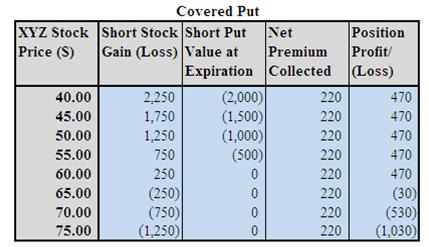
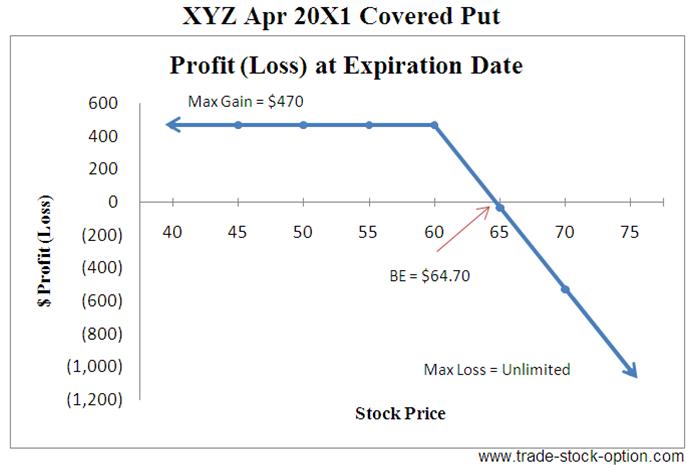
Analysis of Covered Put Example
Maximum Risk
= Unlimited due to the potential rises of the stock price.
Maximum Reward
= [Stock Price Shorted – Put Strike Price] + Put Premium Collected
= ($62.50 - $60 + $2.20) *100 = $470
Breakeven
= Stock Price Shorted add Put Premium Collected
= $62.50 + $2.20 = $64.70
This options strategy enable you to profit from a stock that is range bound, take advantage of contraction in volatility and share in some profit from stock decline. It is primary a bearish strategy but can also profit from a sideway market. Selling an at-the-money Covered Put has the equivalent position of selling an at-the-money Naked Call strategy.
An option position is usually considered to be ”Covered” if there is a fully offsetting market position (in this case, a short stock position). For example, if you short 900 shares of the stock, XYZ, you can write up to 9 put options in a covered put transaction.
A Buy Write (also known as covered put write) strategy is a version of covered put options strategy in which the shorting of stock and sells of put option occur as part of the same transaction. For example, if a stock is trading at $62.50 a share and a put is selling at $2.20, you can enter a single order to execute the transaction at $64.70 a share or better. By entering the limit order in this manner, you can be sure that you will not be executed on one side of the transaction unless the other side is also executed.
Time decay is benefiting you here as it reduces the value of the put options. The last month of an option’s life has the greatest amount of time value erosion occurring. Therefore, selling the premium every month over a period of time will generally earn you a higher return than selling premium a long way out. Provided that the stock does not hit the strike price at expiration date, you will be able to retain the full premium of the stock and start the whole process again the following month.
If you wish to retain your short stock position, then you should select the strike price that is further out of money.
The further the put is out of the money, the lower the possibility of getting assigned and buying back the stock to close off the position.
However, the premium earned is also lower.
If you are comfortable in buying back the stock and close off the position at a price near the current value, you can consider to select the strike price that is at-the-money or in-the-money. In this case, you will be able to earn a higher premium, but this also come with a higher possibility of you being force to buy back the stock.
Do note that an American Style Option can be exercised by the option buyer (holder) at any time before or on the expiration date. Thus if the stock price is below the put strike price, be prepared that you may be exercised to buy back the stock and close off the position… at a profit!!!
The strike price and time frame is an important ingredient in determining the potential risk and reward of a Covered Put strategy. You should pick them according to your risk/reward tolerance and forecast outlook of the underlying stock. Having the patient to wait, knowledge to apply and discipline to follow through the option trading strategies with appropriate risk-reward parameters is important to your long term success in option trading.
Related Strategies
|

|

|
Short Call
|
Bear Put Spread
|
Bear Call Spread
|
Next go to another bearish strategy, Bear Put Spread, to learn how profit can be make from a bearish stock.
Return from Covered Put to Option Strategies



