Long Straddle
Direction: Volatility in Either Direction
Strategy Description
Long Straddle is one of the delta neutral strategies
employed in a highly volatile stock. It usually involves buying At The
Money puts and calls options with the same strike price, expiration date
and underlying stock.
= Long Call (At The Money) + Long Put (At The Money)
Outlook: With this stock option trading strategy, your outlook is directional neutral.
You are expecting an increase in volatility of the underlying stock moving in either direction.
Risk and Reward
Maximum Risk:
- Limited to the Net Premium Paid for the At The Money puts and calls options.
Maximum Reward :
- Potentially unlimited to the upward or downward movement of the underlying stock.
Breakeven :
- Upside Breakeven = Strike Price Plus Net Premium Paid
- Downside Breakeven = Strike Price Less Net Premium Paid
Net Position:
- This is a net debit trade as you are buying the puts and calls options at the same strike price and expiration date.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Potentially unlimited profit potential beyond the breakeven point in either direction.
- Make profit from extremely volatile stocks, without having to determine the direction.
- Limited risk exposure to the net premium paid when the underlying stock is at the strike price on expiration date (where both puts and calls options expired worthless).
Disadvantages:
- Time decay hurts long options as options are a wasting asset. This goes double for this strategy if the strike price, expiration date or underlying stock are badly chosen.
- Significant movement of the stock and options prices is required for this strategy to be profitable.
Exiting the Trade
- If the underlying stock surge up, sell the call options (making a profit for the whole position), and wait for a pull back to profit from the put options.
- If the underlying stock plunge down, sell the put options (making a profit for the whole position), and wait for a retracement to profit from the call options.
- Offset the position by selling both the puts and calls options that you have bought in the first place.
Long Straddle Example
Assumption: XYZ is trading at $25.55 a share on Mar 20X1. The verdict of a legal law suit against the company is expected to be made soon. You are expecting share price of XYZ to soar up or plummet down once the verdict is out. In this case, you may consider to buy one Jun 20X1 $25 strike call at $2.50 and buy one Jun 20X1 $25 strike put at $2.00 to profit from the volatile outlook of the stock. Note: commissions are NOT taken into account in the calculation.
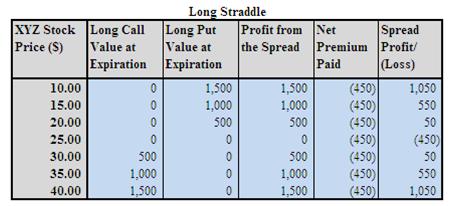
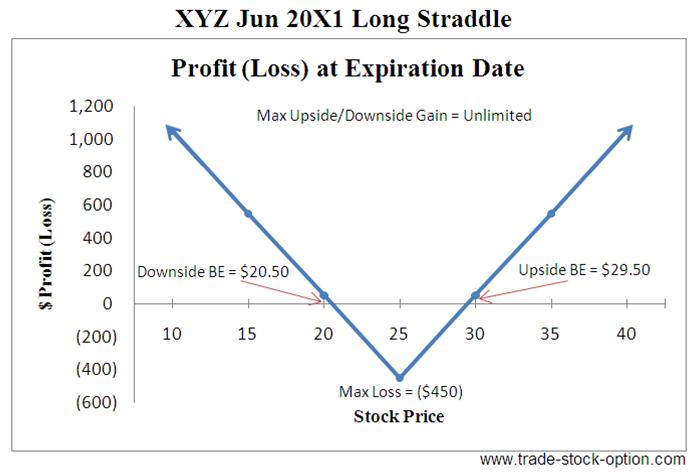
Analysis of Long Straddle Example
Maximum Risk = Limited to the Net Premium Paid = ($2.50 + $2.00) * 100 = $450
Maximum Reward = Potentially unlimited beyond the upside and downside breakeven point of the underlying stock.
Upside Breakeven = Strike Price Plus Net Premium Paid = $25 + $4.50 = $29.50
Downside Breakeven = Strike Price Less Net Premium Paid = $25 - $4.50 = $20.50
This is one of the most popular volatility strategies and easiest to understand. You just need to buy an equal number of puts and calls options of the same strike price and expiration date so that you can make a profit whether the stock move up or down. The good point is, you don’t care which direction it move, as long as it moves sharply in either directions.
For this strategy to be profitable, a rise in the call options value must be able to exceed the fall in the put options value. Or a rise in the put options value must be able to exceed the decline in the call options value. This strategy can be executed at any strike price but is typically established At The Money.
Try to ensure that the implied volatility of the selected stock is currently very low, giving you low option prices, but the stock is about to make an explosively move, just that you are not sure in which direction.
This is a net debit trade as you are paying the premium for both the puts and calls options.
Remembering that the last month of an option’s life has the greatest amount of time value erosion occurring.
Therefore
it is preferably to use this option trading strategy with at least 3
months left to expiration so as to give yourself more time to be right.
This is typically a bet on the volatility expansion. Verdict of law suit, product announcement, earning or economic reports do have a tendency to move the stock price sharply up or down. Some traders prefer to purchase the straddle at a time of low volatility before the announcement and sell at a time of high volatility after the announcement.
You should pick the strike price and time frame of the Long
Straddle according to your risk/reward tolerance and forecast outlook of
the underlying stock. Selecting the option trading strategies with
appropriate risk-reward parameters is important to your long term
success in trading options.
Related Strategies
|

|
|
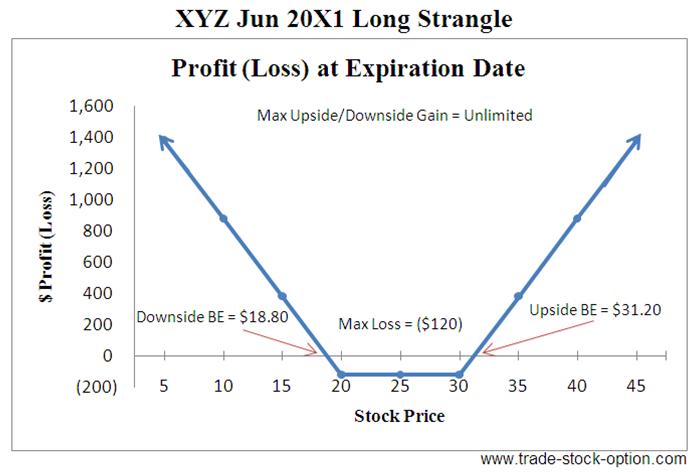
Long Strangle
|
Short Iron Butterfly
|
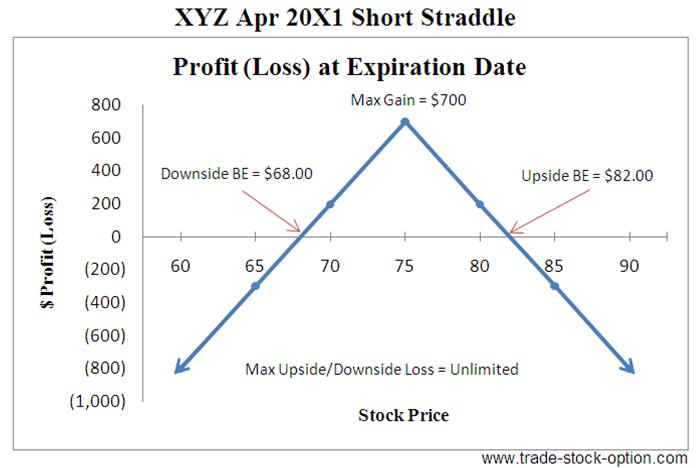
Short Straddle
|
Next go to another volatilities strategy, Long Strangle, to learn how profit can be make from a volatile market.
Return from Long Straddle to Option Strategies



